
|
AISpace2 | Main Tools | News | Downloads | Prototype Tools | Customizable Applets | Practice Exercises | Help | About AIspace |
|
|
Tutorials
Neural Networks
Tutorial 2: Loading a Preexisting Neural NetworkThe Neural Network Applet comes with several pre-defined examples to allow you to start working with graphs without having to create one yourself. To load an example file, go to the 'File' menu and select 'Load Sample Graph and Data'. This will load a graph and its associated data. A dialog box will open with a drop-down menu allowing you to select a particular example. 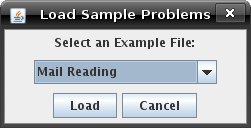
Creating a Neural Network from Data:Neural networks can be created from raw, comma-delimited data.
The only requirement is that the text file must start with a line defining the categories of the data. This line
has to be of the form T:[category1],[category2], ..., [categoryN]; , in the same order as the data. For example,
here
is the data file for "Small Car Database":  Data can also be loaded from from normal applet save files, but it will ignore the graph information and just load the examples. Load a sample data file by going to the 'File' menu and select 'Load Sample
Data'. Once the file is loaded, the Construction Wizard dialog will pop up and query you for information on the neural network that
you want to build. You should input the number of hidden layers needed, and the number of nodes for a
specific hidden layer. Hidden layers can be selected using the pull-down choice menu. The number of nodes default
to 2. This is an example of what the dialog box will look like for the small car database example: 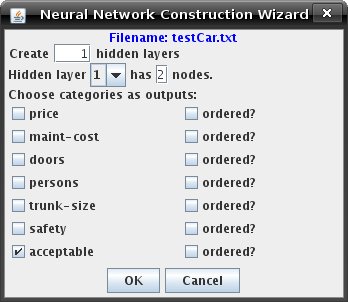 You also have to choose which categories are outputs. Depress the checkbox to the left of the category name to make it an output. Input categories become input nodes, and output categories become output nodes. Also, it may be necessary for some non-numerical categories to be declared as "ordered" by depressing the corresponding checkbox beside the category name. What this means is that this category can be represented as a continuum of numbers. The Wizard will prompt for value mappings for each element of the category. For example, the category "University" with members "SFU, UBC, UVic" cannot be represented as such, but the category "Rating" with members "Low, Medium, High" can be (one can map them as numbers 0, .5, and 1). Numerical categories are already ordered, and hence are not affected if they are declared as ordered. Once you have loaded the small car database example with the Wizard, you may need to move the nodes around to view them better. Your network may look like this: 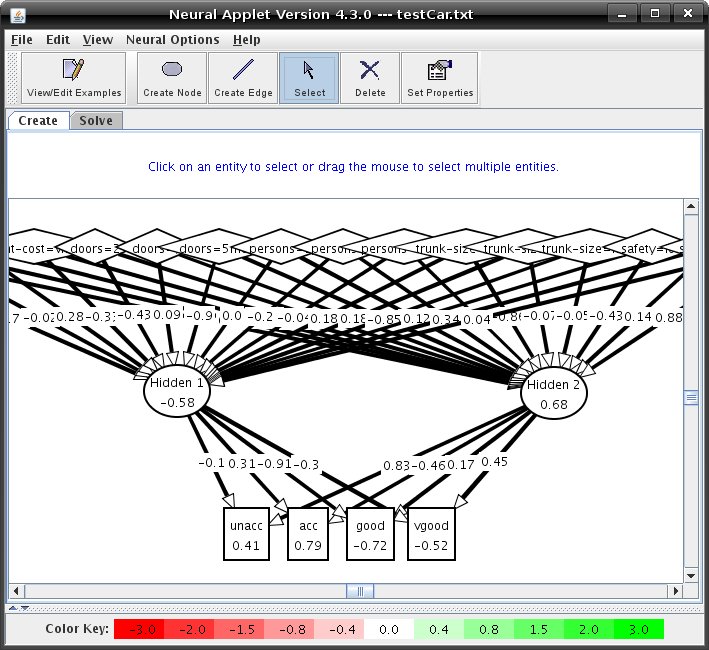 Once all mappings have been declared, the Wizard will create the specified neural network. Also, it will distribute the data into the training sets. You will want to move some examples to the test set. Look at Tutorial 1 on information how to do this. |
| Main Tools: Graph Searching | Consistency for CSP | SLS for CSP | Deduction | Belief and Decision Networks | Decision Trees | Neural Networks | STRIPS to CSP |